| Author | 王平安 |
|---|---|
| pingan8787@qq.com | |
| 博 客 | www.pingan8787.com |
| 微 信 | pingan8787 |
| 每日文章推荐 | https://github.com/pingan8787/Leo_Reading/issues |
| 微信公众号 | 前端自习课 |

这是第三周的练习题,原本应该先发第二周的,因为周末的时候,我的母亲大人来看望她的宝贝儿子,哈哈,我得带她看看厦门这座美丽的城市呀。
这两天我抓紧整理下第二周的题目和答案,下面我把之前的也列出来:
本周练习内容:数据结构与算法 —— LinkedList
这些都是数据结构与算法,一部分方法是团队其他成员实现的,一部分我自己做的,有什么其他实现方法或错误,欢迎各位大佬指点,感谢。
一、链表是什么?与数组有什么区别?生活中有什么案例?
解析:
概念参考阅读 链表 —— 维基百科
1.概念:
链表(Linked list)是一种上一个元素的引用指向下一个元素的存储结构,链表通过指针来连接元素与元素;
链表是线性表的一种,所谓的线性表包含顺序线性表和链表,顺序线性表是用数组实现的,在内存中有顺序排列,通过改变数组大小实现。而链表不是用顺序实现的,用指针实现,在内存中不连续。意思就是说,链表就是将一系列不连续的内存联系起来,将那种碎片内存进行合理的利用,解决空间的问题。
所以,链表允许插入和删除表上任意位置上的节点,但是不允许随即存取。链表有很多种不同的类型:单向链表、双向链表及循环链表。
2.与数组的区别:
相同:
两种结构均可实现数据的顺序存储,构造出来的模型呈线性结构。不同:
链表是链式的存储结构;数组是顺序的存储结构。
链表通过指针来连接元素与元素,数组则是把所有元素按次序依次存储。
链表的插入删除元素相对数组较为简单,不需要移动元素,且较为容易实现长度扩充,但是寻找某个元素较为困难。
数组寻找某个元素较为简单,但插入与删除比较复杂,由于最大长度需要再编程一开始时指定,故当达到最大长度时,扩充长度不如链表方便。
数组和链表一些操作的时间复杂度对比:
数组:
- 查找复杂度:O(1)
- 添加/删除复杂度:O(n)
链表:
- 查找复杂度:O(n)
- 添加/删除复杂度:O(1)
3.生活中的案例:
火车,是由一些列车厢连接起来;
寻宝游戏,每个线索都是下一个线索地点的指针。
二、请事先一个链表,并实现以下方法
append(element):向列表尾部添加一个新的元素。insert(position, element):向列表指定位置插入一个新的元素。remove(element):从列表中移除并返回特定元素(若有多个相同元素则取第一次出现的情况)。indexOf(element):返回元素在列表的索引(若有多个相同元素则取第一次出现的情况),如果列表中没有该元素则返回-1。removeAt(position):从列表中,移除并返回特定位置的一项。isEmpty():如果列表不含任何元素,返回true,否则返回false。size():返回列表中元素个数,与数组的length属性类似。toString():由于列表项使用Node类,需要重写继承自 JavaScript 对象默认的toString()方法,让其只输出元素的值。- 提示:Web 端优先使用 ES6 以上的语法实现。*
解析:
1 | class Node { |
三、实现反转链表
用链表的方式,输出一个反转后的单链表。
示例:
1 | 输入: 1->2->3->4->5->NULL |
解题思路1.使用迭代:
在遍历列表时,将当前节点的 next 指针改为指向前一个元素。由于节点没有引用其上一个节点,因此必须先存储其前一个元素。在更改引用之前,还需要另一个指针来存储下一个节点。不要忘记在最后返回新的头引用!
解题思路2.使用递归:
通过递归修改 head.next.next 和 head.next 指针来实现。
解析:
题目出自:Leetcode 206. 反转链表
介绍两种常用方法:
1.使用迭代:
在遍历列表时,将当前节点的 next 指针改为指向前一个元素。由于节点没有引用其上一个节点,因此必须先存储其前一个元素。在更改引用之前,还需要另一个指针来存储下一个节点。不要忘记在最后返回新的头引用!
1 | /** |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n)。 假设 n 是列表的长度,时间复杂度是 O(n)。
空间复杂度:O(1)。
2.使用递归:
1 | /** |
复杂度分析
时间复杂度:O(n)。 假设 n 是列表的长度,那么时间复杂度为 O(n)。
空间复杂度:O(n)。 由于使用递归,将会使用隐式栈空间。递归深度可能会达到 n 层。
四、判断链表是否有环
设计一个函数 hasCycle,接收一个链表作为参数,判断链表中是否有环。
为了表示给定链表中的环,我们使用整数 pos 来表示链表尾连接到链表中的位置(索引从 0 开始)。 如果 pos 是 -1,则在该链表中没有环。
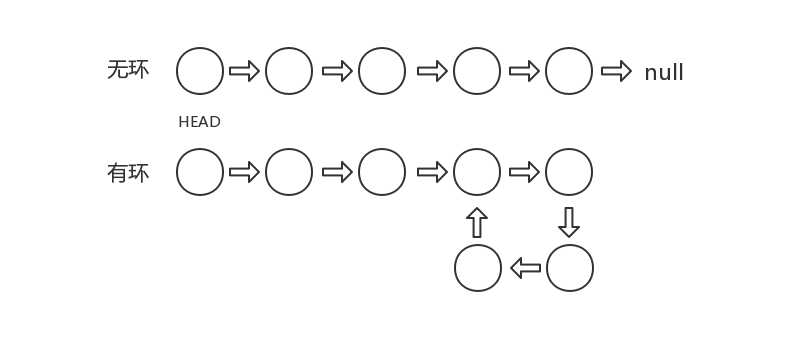
需要注意的是,不可能存在多个环,最多只有一个。
示例 1:
1 | 输入:head = [3,2,0,-4], pos = 1 |
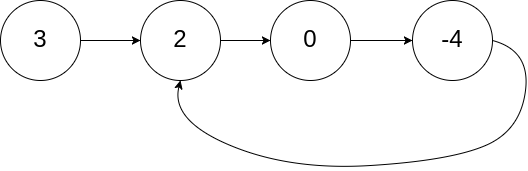
示例 2:
1 | 输入:head = [1,2], pos = 0 |
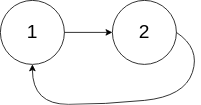
示例 3:
1 | 输入:head = [1], pos = -1 |

解题思路1.判断是否有 null:
一直遍历下去,如果遍历到 null 则表示没有环,否则有环,但是考虑到性能问题,最好给定一段时间作为限制,超过时间就不要继续遍历。
解题思路2.标记法:
也是要遍历每个节点,并在遍历的节点添加标记,如果后面遍历过程中,遇到有这个标记的节点,即表示有环,反之没有环。
解题思路3.使用双指针(龟兔赛跑式):
设置2个指针,一个 快指针 每次走 2 步,慢指针 每次走 1 步,如果没有环的情况,最后这两个指针不会相遇,如果有环,会相遇。
解析:
题目出自:Leetcode 141. 环形链表
1.断是否有 null
1 | /** |
2.标记法
1 | /** |
3.使用双指针
1 | /** |
五、实现两两交换链表中的节点
给定一个链表,两两交换其中相邻的节点,并返回交换后的链表。
你不能只是单纯的改变节点内部的值,而是需要实际的进行节点交换。
示例:
1 | 给定 1->2->3->4, 你应该返回 2->1->4->3. |
解题思路1.使用迭代:
和反转链表类似,关键在于有三个指针,分别指向前后和当前节点,而不同在于两两交换后,移动节点的步长为2,需要注意。
解题思路2.使用递归:
这里也可以使用递归,也可以参考反转链表的问题,终止条件是递归到链表为空,或者只剩下一个元素没得交换了,才终止。
解析:
题目出自:Leetcode 24. 两两交换链表中的节点
介绍两种常用方法:
1.使用迭代:
1 | /** |
2.使用递归:
1 | /** |
